Cross-Border EU E-Invoicing Compliance: What International Businesses Need to Know in 2025
Estimated reading time: 9 minutes
- EN 16931 is mandatory for cross-border B2B and B2G e-invoices across the EU; public administrations must accept it.
- Germany requires e-invoice reception from 1 January 2025 and phases in sending obligations through 2028; it accepts all 24 EU languages.
- ViDA will introduce near-real-time (five-day) cross-border reporting and transaction-level VAT reporting, replacing EC Sales Lists.
- Non-compliance risks include rejected invoices, administrative penalties, delayed payments, and lost procurement opportunities.
- Scalable solutions must handle format conversion (UBL/CII), Peppol connectivity, country-specific authentication, and multilingual output.
Understanding the New Cross-Border E-Invoice Landscape
The EU has reshaped invoice exchange. The E-invoicing Directive (2014/55/EU) requires public administrations to receive invoices using the EN 16931 standard. This creates a common machine-readable baseline so that a supplier in Portugal can technically invoice a government agency in Sweden without format friction.
Reality: implementation differences remain. France uses Chorus Pro, Italy uses SDI, and Germany uses platforms like ZRE and OZG-RE. An EN 16931-compliant invoice can still be rejected if sent via the wrong channel or missing country-specific rules.
Many businesses were surprised when legacy PDF invoices were rejected by public systems — compliance is now the baseline, not an option.
The EN 16931 Standard: Your Foundation for EU Compliance
EN 16931 defines the data model and syntax requirements for structured invoices. In practice this means:
- Mandatory fields must be present in a machine-readable format.
- Conformity levels allow phased implementations depending on technical capability and volume.
- EN 16931 enables interoperability, but many countries add supplementary requirements (digital signatures, archiving rules, specific VAT identifiers).
The standard is the backbone, but not the whole solution: you still need to meet national overlays and transmission rules.
Germany's B2B and B2G Requirements: A Case Study
Germany already mandates electronic invoicing for B2G transactions above €1,000 via the E-Rechnungsgesetz. From 1 January 2025 all German companies must be able to receive e-invoices for domestic taxable B2B transactions. Sending obligations will be phased in through 2028.
Important operational notes:
- Germany accepts invoices in any of the 24 official EU languages, reducing translation burdens for technical validity.
- Platform fragmentation exists by authority level — federal, state, and municipal bodies may use different systems.
- Cross-border suppliers must ensure they meet German reception rules today and prepare for sending obligations by 2028.
ViDA Initiative: The Next Wave of EU B2B/B2G E-Invoicing

ViDA (VAT in the Digital Age) moves the EU toward mandatory e-invoicing for domestic and intra-EU B2B transactions and introduces near-real-time reporting.
Key change: a five-day digital reporting requirement for cross-border sales and purchases that turns invoicing into a tax compliance stream instead of a periodic task.
ViDA will replace the EC Sales List with transaction-level reporting. This increases data volume dramatically for businesses with many invoices and forces systems to be fast, reliable, and continuously connected.
Technical Challenges in Cross-Border E-Invoice Implementation
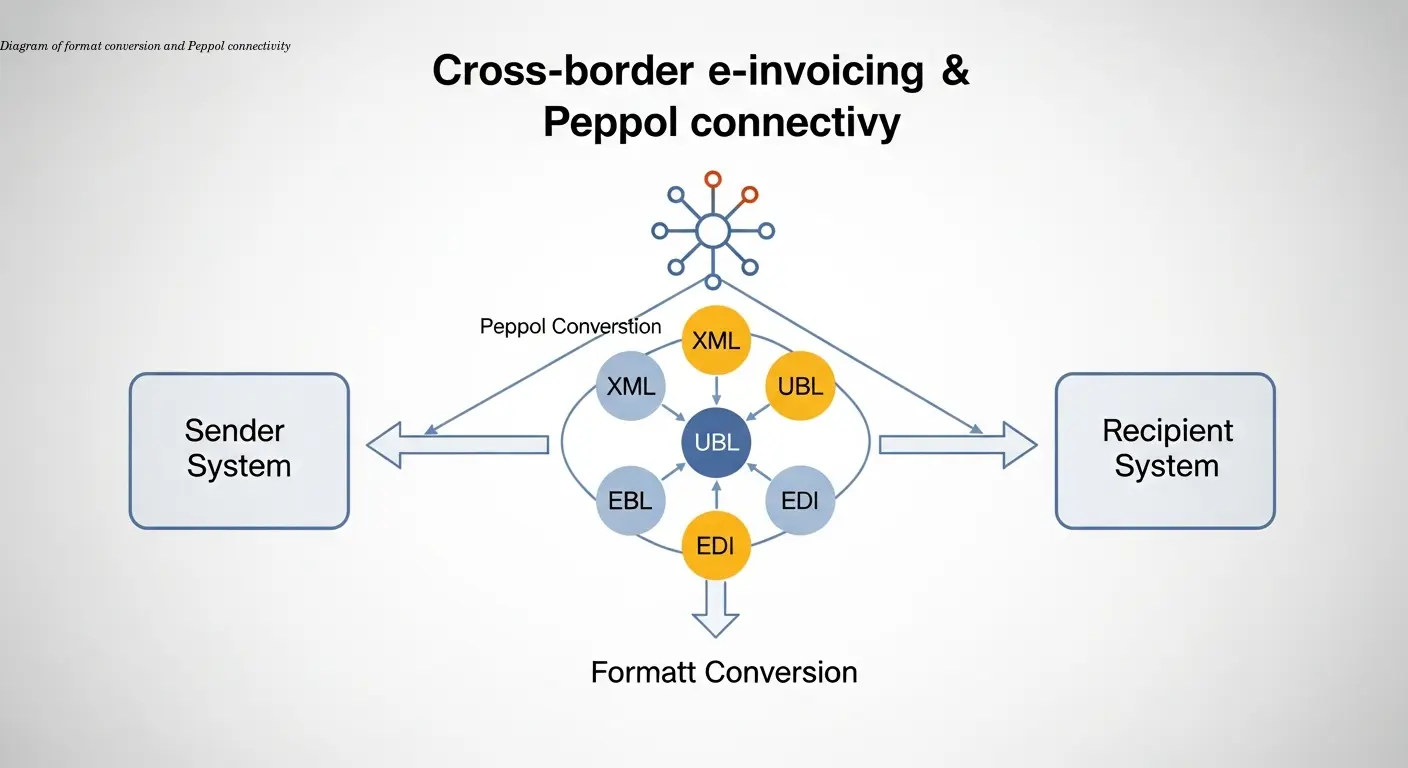
Major technical hurdles:
- Format translation: EN 16931 is data-centric but accepts multiple syntaxes (UBL, CII). Your system must produce the required format per destination.
- Network connectivity: Peppol is the dominant transport network; connecting requires an access point provider and configuration.
- Authentication & archiving: country-specific certificate authorities, signature rules, and retention standards vary.
- Testing: each national connection often requires separate validation and certification cycles.
- Language & documentation: technical specs and error messages are often in local languages — budget for translation resources.
Compliance Risks and Practical Implications for International Trade
Non-compliance has immediate commercial impacts:
- Rejected invoices delay payments and can extend payment cycles to 90 days or more.
- Administrative penalties and VAT validity issues may arise, affecting both supplier and buyer VAT deductions.
- Smaller exporters often face disproportionate burdens despite lower transaction counts.
- Competitive disadvantage in public procurement if you cannot integrate digitally.
As ViDA arrives, the margin for error decreases — real-time reporting surfaces problems immediately.
Building a Scalable Solution for EU E-Invoicing Requirements

A sustainable approach requires flexibility and integration:
- Assess whether your ERP can produce structured data in multiple formats and route invoices by country-specific rules.
- Consider cloud-based platforms that handle format conversion, network connections (Peppol), and compliance updates for you.
- Ensure multilingual invoice generation and accurate master data (customer details, VAT IDs, product codes).
- Adopt a phased rollout: start with high-volume or strategic trading partners, then expand.
- Automate integration between order, fulfillment, and accounting systems to avoid manual transformation steps.
Preparing Your Business for the Future of Cross-Border Invoicing

Actionable steps to get ready:
- Audit current processes: list every country you invoice into, platforms used, and past compliance issues.
- Talk to customers: ask about their receiving systems and timelines — many implement ahead of legal deadlines.
- Build or source skills: technical e-invoicing knowledge differs from traditional accounting; engage specialists if needed.
- Choose partners: access point providers, compliance consultants, and software vendors can speed adoption.
- Test continuously: as rules and systems evolve, regular validation prevents surprises.
FAQ
What exactly is a cross-border e-invoice in the EU context?
A cross-border e-invoice is an electronic invoice that meets EN 16931 standards and is sent between businesses or from businesses to government entities located in different EU member states. It must be in a structured, machine-readable format rather than just a PDF or scanned document.
Do I need different systems for B2B and B2G e-invoicing?
Not necessarily. While B2G transactions often require sending invoices through specific government platforms, the underlying data format (EN 16931) remains the same. A properly designed system can handle both transaction types, though you may need different transmission methods for each.
Can I still send invoices in my own language to customers in other EU countries?
Germany and several other EU countries accept invoices in any of the 24 official EU languages. However, regulations vary by country, and providing invoices in your customer's language is often appreciated even when not legally required.
What happens if my e-invoice doesn't meet the technical requirements?
Non-compliant invoices will typically be rejected by the receiving system. This delays payment, may require manual intervention to correct, and in some cases can result in administrative penalties. Repeated compliance failures can damage customer relationships and disqualify you from public procurement opportunities.
When do the ViDA requirements take effect?
The ViDA initiative is still being finalized at the EU level, with implementation timelines varying by member state. Businesses should monitor announcements from the European Commission and their national tax authorities for specific deadlines affecting their operations.
Do small businesses have the same e-invoicing obligations as large corporations?
Generally yes, once mandates take effect in each country. Some jurisdictions may provide transition periods or simplified processes for smaller businesses, but the trend is toward universal requirements regardless of company size.
How much does it cost to implement cross-border e-invoice compliance?
Costs vary widely based on transaction volumes, number of countries involved, and existing technical infrastructure. Options range from low-cost cloud services for simple needs to enterprise implementations requiring significant investment. Most businesses find the efficiency gains offset implementation costs over time.
Can I create compliant cross-border e-invoices without expensive enterprise software?
Yes, several web-based tools offer affordable EU-compliant e-invoice creation and transmission. These solutions handle the technical formatting and validation requirements without requiring extensive IT infrastructure or expertise on your part.
