Automating B2G E-Invoicing: A Practical Guide for Government Suppliers
Estimated reading time: 9 minutes
Key takeaways
- B2G e-invoice creation is mandatory for suppliers working with government entities in Germany and across the EU, requiring structured digital formats like XRechnung
- Automation cuts down manual errors, speeds up payment cycles, and ensures compliance with federal and state regulations
- Government invoice submission uses dedicated portals (ZRE, OZG-RE) or the Peppol network for secure, validated transmission
- From January 2025, most businesses in Germany must handle e-invoices for B2B transactions, expanding digital requirements beyond just B2G
- Automated systems integrate with your existing ERP software, handling everything from generation to archiving without constant manual oversight
Table of contents
What B2G E-Invoicing Actually Means for Your Business
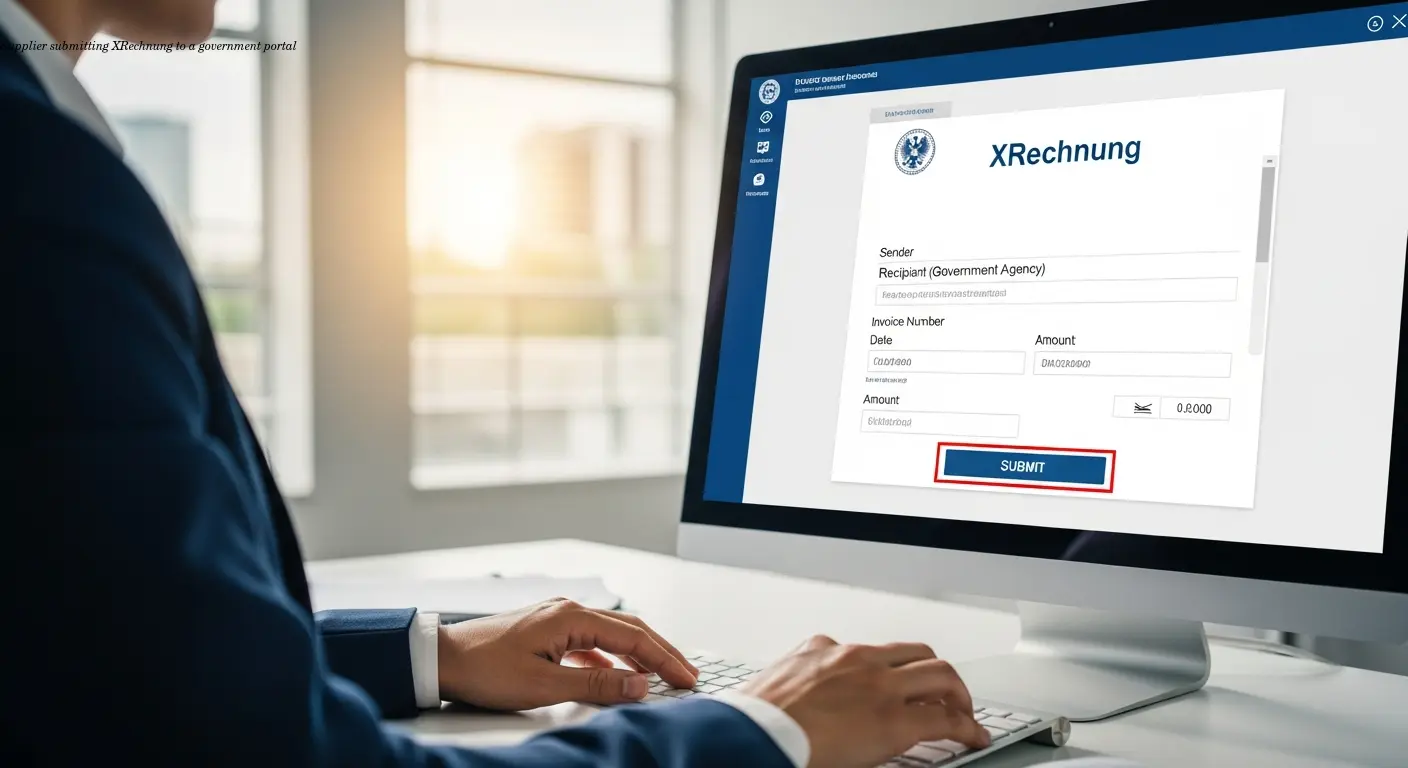
If you're supplying goods or services to government entities, you've probably heard about B2G e-invoicing by now. The term refers to electronic invoice submission directly to public sector organizations using specific digital formats that meet regulatory standards. In Germany, this isn't optional anymore—it's a legal obligation for any supplier working with federal, state, or municipal authorities on contracts typically above €1,000.
What makes B2G different from regular B2B invoicing is the strict format requirements and the designated submission channels you need to use. Government bodies need invoices in structured formats, primarily XRechnung, which complies with the European Norm EN 16931. You can't just send a PDF anymore and call it done.
I remember a supplier who'd been sending PDF invoices to a municipal office for months, only to find out none of them were being processed. The backlog cost them serious cash flow problems that could've been avoided with proper B2G e-invoice creation from the start.
The scope covers all levels of government administration in Germany. Your invoices need to contain specific mandatory fields including invoice number, complete supplier data, VAT details, and service descriptions. Missing even one element can trigger automatic rejection.
Why Automation Changes Everything for Government Invoice Submission
Manual invoicing for government contracts is a recipe for delays and errors. When you're dealing with strict format requirements and multiple validation rules, automation becomes less of a luxury and more of a necessity. Automated B2G e-invoice creation handles repetitive tasks—generation, validation, formatting, and submission—without constant human intervention.
The benefits show up immediately:
- Processing times drop because automated systems catch errors before submission
- Cash flow improves when invoices get processed faster
- Integration with ERP systems prevents manual re-entry errors
- Real-time tracking shows exactly where each invoice sits in the approval process
I've seen businesses cut their average payment wait time by nearly 30% just by switching to automated submission.
Understanding German B2G Requirements and Platforms
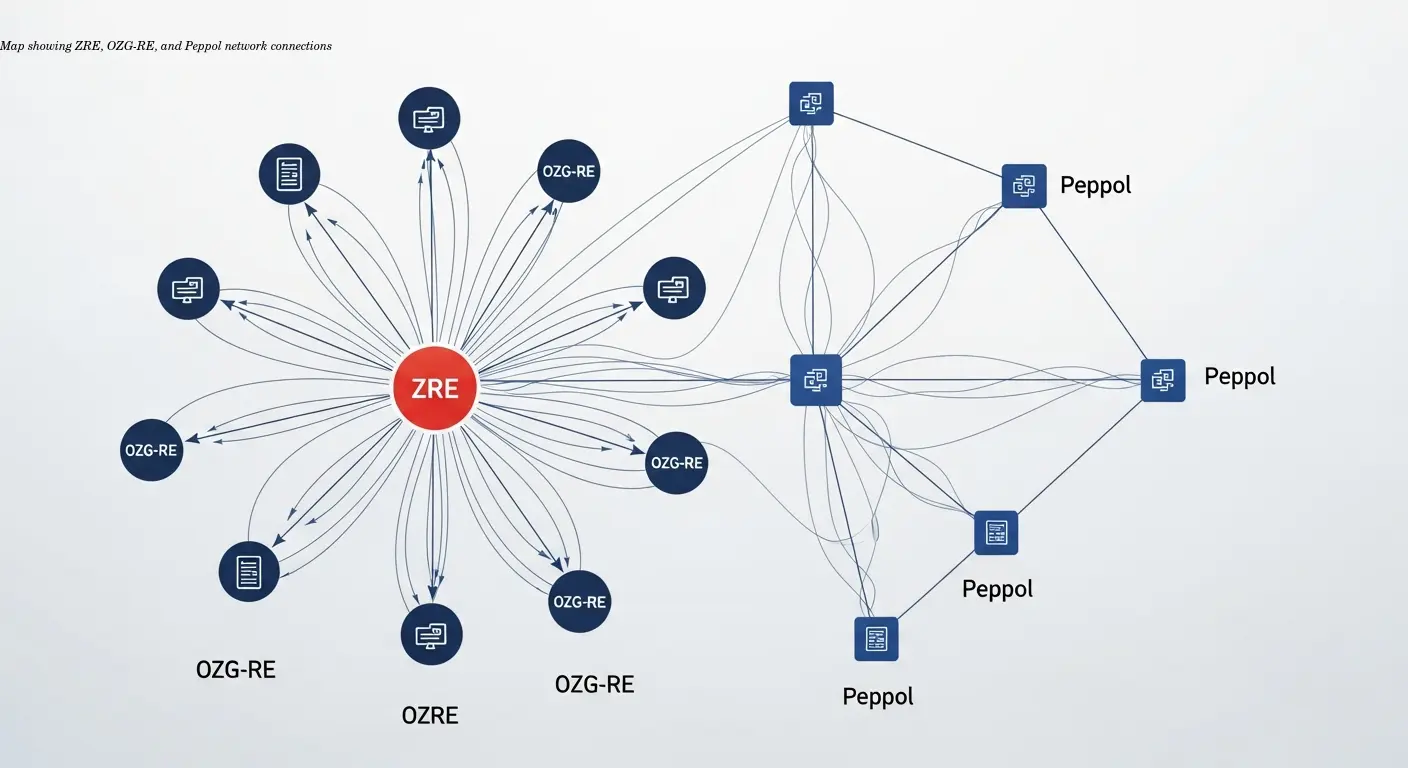
Germany's B2G e-invoicing rollout started at federal level in 2020 and expanded across states and municipalities. Two primary platforms are critical:
- ZRE (Zentrale Rechnungseingangsplattform des Bundes) — central invoice entry for federal administration
- OZG-RE — covers a broader range of public entities under the Online Access Act
Both platforms require invoices in XRechnung, an XML-based file format that follows EN 16931. Submission methods include direct portal upload, designated email addresses, or the Peppol network, which enables standardized exchange across Europe.
Each invoice undergoes immediate validation on submission for completeness, correct formatting, and mandatory fields. If something's wrong, you get feedback straight away so you can correct and resubmit.
The Technical Process of Automated B2G E-Invoice Creation
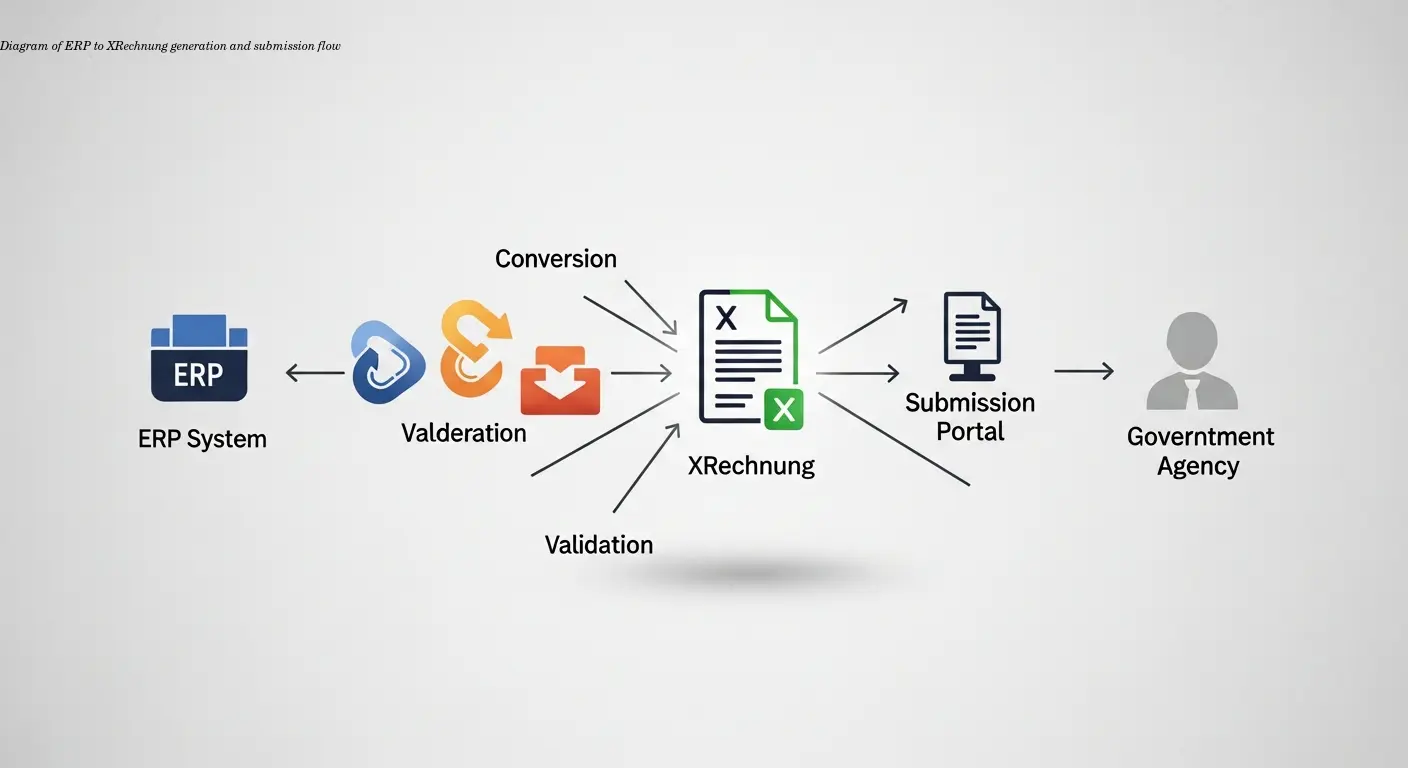
Automation follows a clear sequence: your ERP captures transaction data, an automation engine generates XRechnung files, and secure connections submit them to government platforms. The software applies rules for mandatory fields, date formats, and VAT calculations automatically.
Connections to ZRE, OZG-RE, or Peppol are authenticated and secure. Submission triggers government-side validation; you receive confirmations for accepted invoices or detailed error messages for resubmission. Full lifecycle tracking shows receipt, validation status, approval progress, and payment initiation.
Archiving is handled electronically to meet German retention rules (up to 10 years), preserving file integrity, signatures, and timestamps for audits.
Compliance, Validation, and Staying on the Right Side of Regulations

Compliance is both a technical and legal requirement. The E-Rechnungsgesetz sets the framework while federal and state regulations provide implementation details. Mandatory fields include business registration, tax ID, unique invoice number, dates, full descriptions, prices, VAT rates, and totals. Missing any of these leads to automatic rejection.
VAT handling is critical: automated systems must apply correct rates, tax codes, and handle cross-border rules like reverse charge. Digital signatures, while not always mandatory, add authenticity and non-repudiation and should be supported by your solution.
Validation occurs at multiple levels: your software first checks XML structure and required fields, then the government platform performs its validations. Because regulations change, automation vendors update rules centrally so you stay compliant without manual chasing.
Expanding Requirements: From B2G to Broader B2B E-Invoicing
Germany is extending electronic invoicing beyond B2G. From January 2025, businesses established in Germany must be able to receive e-invoices for domestic B2B transactions. Sending requirements will phase in later, but the direction is clear: electronic invoicing becomes standard.
This shift increases the value of automation. If you're set up for XRechnung, extending capabilities to cover B2B workflows is a logical next step. The Peppol network also helps by enabling cross-border invoicing through a single standard connection.
Practical Implementation: Getting Your Automation Running

You typically don't need a full systems overhaul. Check whether your ERP or accounting software already supports XRechnung generation. If not, dedicated platforms connect via APIs or file imports and handle formatting and submission.
Key steps:
- Assess current systems and identify gaps
- Enable built-in XRechnung settings or integrate a dedicated solution
- Test thoroughly in government test environments with varied scenarios
- Train staff to interpret validation messages and monitor invoice status
- Migrate gradually—start with new contracts and phase in older ones
Responsive vendor support is essential because regulations and platform requirements change and technical issues occur.
Real Benefits and What to Expect from Automation

Automation brings measurable improvements: faster processing, fewer rejections, lower labor costs, and better scalability. Errors caused by manual entry disappear because data flows directly from source systems into validated, structured invoices.
Other outcomes:
- Cost savings from reduced manual processing and fewer correction cycles
- Scalability—handle growth without proportional administrative hires
- Improved compliance confidence and audit readiness
- Better relationships with government customers due to reliable submissions
Electronic archiving and complete metadata make audits straightforward: retrieval is instant and well-documented.
FAQ
What is b2g e-invoice creation?
B2G e-invoice creation is the process of generating and submitting invoices electronically to government entities using specific structured formats like XRechnung. It's mandatory for suppliers working with public sector organizations in Germany and requires compliance with technical standards defined in EN 16931.
Do I really need automation for government invoice submission?
While you can technically create and submit B2G invoices manually, automation drastically reduces errors, saves time, and ensures compliance. Given the strict validation requirements and the expanding scope of e-invoicing requirements into B2B, automation becomes increasingly necessary rather than optional for efficient operations.
What platforms do I use to submit invoices to German government entities?
The main platforms are ZRE (Zentrale Rechnungseingangsplattform des Bundes) for federal agencies and OZG-RE for other public entities. You can also use the Peppol network for electronic transmission. The specific platform depends on which government entity you're invoicing.
What format must my invoices be in?
For B2G invoicing in Germany, XRechnung is the primary required format. This is a structured XML-based format that complies with the European standard EN 16931. Simple PDFs or other unstructured formats don't meet the requirements for government invoice submission.
What happens if my invoice gets rejected?
Government platforms provide immediate feedback when validation fails, explaining what's wrong. You can correct the issues and resubmit. Automated systems help prevent rejections by validating invoices before submission, catching problems early in the process.
When did B2G e-invoicing become mandatory in Germany?
Federal-level B2G e-invoicing became mandatory in 2020. State and municipal requirements rolled out on various schedules, but by now the obligation covers all levels of government administration for contracts above typical thresholds around €1,000.
How does the January 2025 B2B requirement affect me?
From January 2025, businesses in Germany must be able to receive e-invoices for domestic B2B transactions. Sending requirements phase in later. This means your invoicing systems need to handle both B2G and B2B electronic invoices, making automation even more valuable.
Can I use the same system for B2G and B2B invoices?
Yes, many automated invoicing solutions handle both B2G and B2B requirements. While the specific formats might vary slightly, the core capabilities—structured data, validation, electronic transmission, archiving—apply to both types of transactions.
What are the mandatory fields for a German B2G invoice?
Required fields include invoice number, invoice and delivery dates, complete supplier details, tax identification number, description of goods or services, quantities and prices, applicable VAT rates and amounts, and total invoice amount. The XRechnung format enforces these requirements technically.
How long do I need to keep electronic invoices?
German tax law requires invoice retention for up to 10 years. Electronic invoices must be archived in their original format, maintaining integrity and authenticity. Automated systems handle this archiving requirement as part of the invoice lifecycle.
